30 Loneliness Statistics: How Many People are Lonely?
January 10, 2024
Discover shocking loneliness statistics and the impact on mental health. Unveiling the hidden epidemic.

TOP 10 Loneliness Statistics Facts
Loneliness is a common experience that can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or social status. Here are the top 10 loneliness statistics facts:
- Over 60% of people feel lonely. According to a survey conducted by the American Association of Retired Persons (AARP), more than 60% of adults report feeling lonely at some point in their lives.
- Loneliness is more common among young adults. A study published in the Journal of Social and Personal Relationships found that people aged 18 to 34 are more likely to feel lonely than older adults.
- Social media can contribute to loneliness. Despite its promise of connecting people, social media can actually increase feelings of loneliness and isolation, according to a study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
- Loneliness can increase the risk of mortality. A meta-analysis of studies involving more than 3 million participants found that loneliness and social isolation are associated with a significantly increased risk of premature death.
- Loneliness can affect mental health. People who feel lonely are more likely to experience depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems, according to a study published in the Journal of Health and Social Behavior.
- Loneliness can affect physical health. Loneliness has been linked to a range of physical health problems, including cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer's disease, and stroke.
- Loneliness can be contagious. A study published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology found that loneliness can spread through social networks, much like a virus.
- Loneliness can be treated. There are a variety of effective treatments for loneliness, including therapy, social support, and volunteering.
- Loneliness is not the same as being alone. People can feel lonely even when surrounded by others, and conversely, people can enjoy being alone without feeling lonely.
- Loneliness is a growing public health concern. As rates of loneliness continue to rise, many health experts are calling for increased attention and resources to address this important public health issue.

TOP 10 Loneliness Statistics Facts Worldwide
Loneliness is not just a problem in one country or region, it is a global issue that affects people all around the world. Here are the top 10 loneliness statistics facts worldwide:
- Loneliness is prevalent across the globe. Studies show that loneliness affects people from all cultures and countries, regardless of socioeconomic status.
- In some countries, young people are particularly vulnerable to loneliness. In Japan, for example, hikikomori is a phenomenon where young people isolate themselves from society and family for months or even years at a time due to social anxiety and fear of failure.
- Loneliness can be especially acute for older adults in many parts of the world. In China, for instance, many elderly individuals live alone as their children have moved away to pursue work opportunities in urban areas.
- Women tend to experience loneliness more frequently than men worldwide. A study conducted by YouGov found that women were more likely than men to report feeling lonely in nearly every country surveyed.
- Poverty and social isolation are strongly linked worldwide. Individuals who live in poverty are often more socially isolated and therefore more likely to experience feelings of loneliness.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated feelings of loneliness globally. With lockdowns and social distancing measures in place around the world, many people have been cut off from their usual sources of social support.
- Immigrants and refugees may experience heightened levels of loneliness when moving to new countries. The process of adapting to a new culture and language can be isolating, particularly if support systems are lacking.
- Loneliness can affect students studying abroad worldwide. Being separated from friends and family can make international students feel disconnected from their new environment.
- Developing strong social connections is key to combatting global loneliness rates. Encouraging community-building activities and initiatives can help individuals build meaningful relationships.
- Addressing loneliness on a global scale requires collaboration and investment from governments, healthcare systems, and communities worldwide. By prioritizing social connectedness as a public health issue, we can work towards creating a world where everyone has access to the social support they need.
TOP 10 Loneliness Statistics By Country
Loneliness is a global issue that affects people from all walks of life. Here are the top 10 loneliness statistics by country:
- United States: In the US, over 35% of adults aged 45 and older report feeling lonely at least some of the time, according to a study by AARP.
- Japan: Japan has one of the highest rates of social isolation in the world, with over half a million elderly people estimated to be living in complete isolation.
- India: A survey conducted by The Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations found that 43% of respondents felt lonely often or always.
- Australia: According to a survey conducted by Swinburne University, one in four Australians feel lonely on three or more days each week.
- Canada: A study by Angus Reid Institute found that one in five Canadians feel lonely often or always.
- United Kingdom: In the UK, over nine million people report feeling lonely at least some of the time, according to a survey conducted by The Co-op and British Red Cross.
- China: China has seen a rapid increase in loneliness rates due to urbanization and changing societal norms that have weakened traditional social networks.
- Spain: Over 30% of Spaniards live alone, making it one of the most socially isolated countries in Europe.
- Brazil: A survey conducted by Cigna found that nearly half of Brazilians reported feeling isolated and disconnected from others.
- South Africa: A study published in BMC Public Health found that nearly 40% of South African adolescents reported feeling lonely.
These statistics highlight how loneliness affects different populations around the world and demonstrate the need for increased attention and resources towards addressing this important public health concern globally.
Loneliness Statistics By Age
Loneliness is a universal experience that can affect people of all ages, but research suggests that certain age groups may be more vulnerable than others. Here are some loneliness statistics by age:
- Young Adults: People aged 18 to 34 are more likely to feel lonely than older adults, according to a study published in the Journal of Social and Personal Relationships.
- Middle-aged Adults: A survey conducted by Cigna found that middle-aged adults (ages 35-49) reported higher levels of loneliness than any other age group.
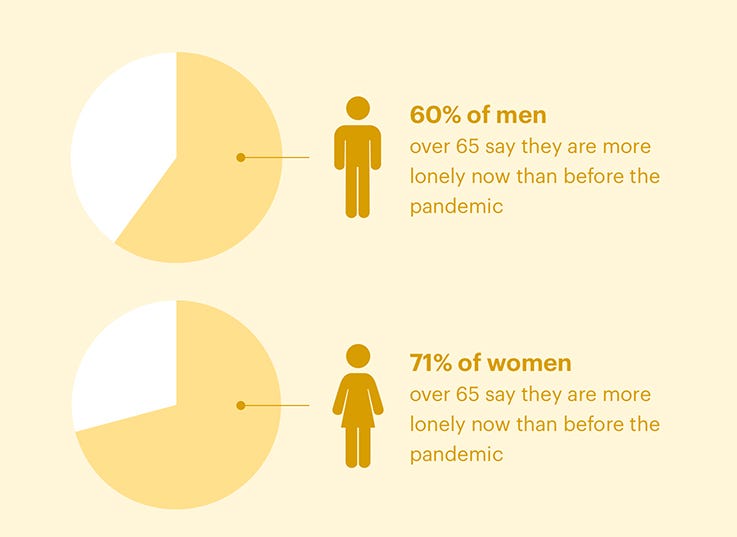
- Older Adults: Loneliness is a significant issue for many older adults, particularly those who live alone or have limited social support. According to a report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, nearly one-quarter of Americans aged 65 and older are considered socially isolated.
These statistics suggest that loneliness affects different age groups differently and highlight the need for targeted interventions that take into account the unique challenges faced by individuals at different stages of life.
Loneliness Statistics By Gender
Gender is another factor that can influence an individual's experience of loneliness. Here are some loneliness statistics by gender:
- Women: Women tend to experience loneliness more frequently than men, according to a study conducted by YouGov. The study found that women were more likely than men to report feeling lonely in nearly every country surveyed.
- Men: While women may be more likely to feel lonely, men may be less likely to seek help for their feelings of isolation. A survey conducted by the Campaign to End Loneliness found that 35% of men over the age of 50 said they felt lonely at least once a week, but only 18% had discussed their feelings with someone else.
- Non-binary individuals: There is limited research on how non-binary individuals experience loneliness, but it is clear that they face unique challenges when it comes to social connection and community building. Non-binary individuals may struggle to find spaces where they feel accepted and understood, which can contribute to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
These statistics suggest that gender plays an important role in shaping an individual's experience of loneliness and highlight the need for interventions and support systems that are tailored to the specific needs of different genders.
The Loneliness Epidemic
Loneliness is a pervasive issue that affects individuals across the globe. Understanding the nature of loneliness and its impact on mental health is crucial in addressing this growing epidemic.
Understanding Loneliness
Loneliness can be defined as a subjective feeling of social isolation or lack of connection with others. It is important to note that loneliness is not solely determined by the number of social interactions one has, but rather the quality and depth of those connections. An individual can feel lonely even when surrounded by others if they lack meaningful relationships or a sense of belonging.
Loneliness is a complex emotional state that can stem from various factors, including social, psychological, and environmental aspects. It can arise from factors such as a lack of social support, living alone, experiencing a major life change, or having limited social interactions. It is not limited to any specific age group, gender, or demographic, as anyone can experience loneliness.
The Impact of Loneliness on Mental Health
Loneliness can have profound effects on mental health, leading to various emotional and psychological challenges. Prolonged feelings of loneliness and social isolation can contribute to increased levels of stress, anxiety, and depression. Individuals who experience chronic loneliness may also be at a higher risk of developing mental health disorders.
Research has shown that loneliness can disrupt sleep patterns, impair cognitive functions, and weaken the immune system. It can also contribute to a decline in overall well-being and quality of life. The negative impact of loneliness on mental health highlights the importance of addressing this issue and providing support to those who are affected.
By recognizing the impact of loneliness on mental health, we can work towards developing strategies and interventions to combat this epidemic and create a more connected and supportive society.
Loneliness and Social Media
In today's digital age, social media platforms have become an integral part of our lives. While they promise to connect us with others, there is a paradoxical relationship between social media and loneliness. Let's explore the paradox of connection and the role of social media in loneliness.
The Paradox of Connection
Social media platforms provide us with seemingly endless opportunities to connect with others. We can easily share our thoughts, experiences, and photos, and receive instant feedback from our friends and followers. These platforms create a sense of virtual community and offer the illusion of being constantly connected.
However, the paradox lies in the fact that despite this increased connectivity, feelings of loneliness and isolation have been on the rise. The virtual connections formed through social media often lack the depth and authenticity of real-life relationships. It's important to recognize that online interactions cannot fully replace the richness and complexity of face-to-face interactions that humans need for true connection and belonging.
Social Media's Role in Loneliness
While social media can provide a sense of belonging and connection, it can also contribute to feelings of loneliness. Here are some ways in which social media can impact loneliness:
- Social Comparison: On social media, people tend to present a curated version of their lives, showcasing their best moments and achievements. This can lead to social comparison, where individuals compare their own lives to the seemingly perfect lives of others. This constant comparison can evoke feelings of inadequacy, loneliness, and isolation.
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Social media platforms often display a highlight reel of what others are doing, which can trigger a fear of missing out. Seeing others engaging in social activities or events can intensify feelings of loneliness for those who are not partaking in similar experiences.
- Reduced Face-to-Face Interaction: Spending excessive time on social media can lead to a decrease in in-person interactions. This can result in fewer opportunities for meaningful connections and conversations, contributing to feelings of loneliness and social isolation.
- Superficial Connections: While social media allows us to connect with a larger number of people, these connections are often superficial and lack the depth that comes with real-life relationships. The absence of non-verbal cues and physical presence can limit the emotional connection we feel with others.
It's important to note that social media's impact on loneliness can vary among individuals. Some people may find solace and support through online communities and virtual connections, while others may experience increased feelings of loneliness. Understanding the complexities of social media's role in loneliness can help individuals navigate these platforms more mindfully.
When addressing loneliness, it's essential to strike a balance between online and offline interactions. Real-life connections and meaningful relationships play a vital role in combating loneliness.
Loneliness and Health
Loneliness not only affects our emotional well-being but also has significant implications for our physical and mental health. The consequences of loneliness can manifest in both physical and mental health domains. Let's explore the impact of loneliness on these aspects.
Physical Health Consequences of Loneliness
Loneliness has been linked to various physical health problems. Studies have shown that individuals who experience chronic loneliness may be at a higher risk of developing certain health conditions. Here are some notable physical health consequences associated with loneliness:
Physical Health Consequences of Loneliness
Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as high blood pressure and heart disease
Weakened immune system, leading to increased susceptibility to infections
Poor sleep quality and sleep disturbances
Altered stress response, potentially leading to chronic stress
Increased inflammation in the body, which is associated with various health problems
It's important to note that loneliness alone may not directly cause these physical health conditions, but rather, it can contribute to an increased risk or exacerbate existing health issues.
Mental Health Consequences of Loneliness
Loneliness can have a profound impact on mental health. The feeling of isolation and disconnection from others can contribute to the development or worsening of various mental health conditions. Some of the mental health consequences associated with loneliness include:
Mental Health Consequences of Loneliness
Increased risk of depression and anxiety disorders
Higher rates of stress and chronic psychological distress
Decreased self-esteem and feelings of worthlessness
Difficulty in managing emotions and regulating mood
Greater likelihood of experiencing cognitive decline and dementia in older adults
Loneliness can be particularly challenging for certain population groups, such as the elderly or individuals who identify as LGBTQ+.
Understanding the physical and mental health consequences of loneliness is crucial in addressing this widespread issue. By recognizing the impact of loneliness on our overall well-being, we can take steps to combat loneliness and promote healthier connections and social support networks.
Combating Loneliness
Addressing the loneliness epidemic requires collective efforts from individuals, communities, and governments. By implementing strategies at both personal and societal levels, we can combat loneliness and foster a sense of connection and belonging.
Strategies for Individuals
Individuals can take proactive steps to combat loneliness in their own lives. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Cultivate meaningful relationships: Invest time and effort in building and nurturing relationships with family, friends, and colleagues. Engage in activities together, communicate regularly, and express genuine care and support.
- Expand social networks: Seek out opportunities to meet new people and expand your social circle. Join clubs, attend community events, or participate in hobbies and interests that align with your passions.
- Utilize technology for connection: While technology can contribute to feelings of loneliness, it can also be used as a tool for connection. Stay connected with loved ones through video calls, messaging apps, or online communities. However, it's important to strike a balance and not rely solely on virtual interactions.
- Practice self-care: Prioritize self-care by engaging in activities that bring you joy and relaxation. This can include exercise, hobbies, meditation, or any other activity that promotes physical and mental well-being.
- Seek professional help: If feelings of loneliness persist or become overwhelming, consider seeking support from mental health professionals. They can provide guidance and strategies to navigate loneliness and improve overall well-being.
Conclusion
As we have explored in this article, loneliness is a complex and widespread issue that can have profound effects on our physical, emotional, and mental well-being. However, by recognizing the impact of loneliness and taking proactive steps to combat it, we can create a more connected and supportive society.
It's essential to remember that loneliness is not a personal failure or weakness but rather a societal issue that requires collective effort. By cultivating meaningful relationships, expanding our social networks, utilizing technology mindfully, practicing self-care, and seeking support when needed, we can combat loneliness and promote overall well-being.
As we move forward towards creating a more connected world, let's continue to prioritize empathy, kindness, and compassion towards ourselves and others. By doing so, we can build stronger communities and foster a sense of belonging for all individuals.
Sources:
https://medium.com/@kimmurray96/elderly-loneliness-f9e344bff600
https://ourworldindata.org/social-connections-and-loneliness
https://edition.cnn.com/2023/10/24/health/lonely-adults-gallup-poll-wellness/index.html
https://www.cdc.gov/aging/publications/features/lonely-older-adults.html
https://www.apa.org/monitor/2023/07/young-adults-lonely-pandemic
https://www.verywellmind.com/loneliness-causes-effects-and-treatments-2795749









