Steps of CBT
January 10, 2024
Master mental resilience with step-by-step cognitive behavioral therapy. Unveil the power of CBT for a resilient mind.

Introduction to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and effective form of psychotherapy that focuses on the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It is based on the premise that our thoughts and beliefs influence our emotions and actions. By identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, individuals can develop healthier ways of thinking and improve their mental resilience.
What is CBT?
CBT is a goal-oriented and practical approach to therapy that aims to help individuals understand and modify their thoughts and behaviors. It involves collaborative work between a therapist and the individual, where they work together to identify and address specific challenges.
Through CBT, individuals learn to recognize and change negative thought patterns that contribute to distressing emotions and unhelpful behaviors. By challenging irrational beliefs and developing more balanced and realistic thinking, individuals can experience improvement in their overall well-being.
The Role of CBT in Mental Resilience
Mental resilience refers to an individual's ability to adapt and cope with stress, adversity, and challenges. CBT plays a significant role in enhancing mental resilience by equipping individuals with the necessary tools and strategies to manage their thoughts and emotions effectively.
By working through the various steps of CBT, individuals learn to identify negative thoughts and beliefs, understand how these thoughts influence their feelings and behaviors, and restructure their thinking patterns to foster healthier cognition. Additionally, CBT helps individuals develop coping strategies and implement self-care practices that contribute to ongoing maintenance of mental well-being.
CBT can be beneficial for a wide range of mental health concerns, including anxiety, depression, insomnia, eating disorders, anger management, and more.
By understanding the fundamental principles of CBT and its role in promoting mental resilience, individuals can embark on a journey of self-discovery and growth, ultimately improving their overall psychological well-being.
Step 1: Identifying Negative Thoughts and Beliefs
In the first step of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), individuals learn to identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to their emotional distress. This process involves recognizing negative thought patterns and actively challenging the validity of these beliefs.
Recognizing Negative Thought Patterns
To begin the journey towards mental resilience, it is essential to become aware of negative thought patterns that may be causing or exacerbating emotional distress. Negative thought patterns often manifest as automatic, recurring thoughts that contribute to negative emotions and unhelpful behaviors.
Some common types of negative thought patterns include:
- Catastrophizing: Magnifying the negative aspects of a situation and expecting the worst possible outcome.
- Overgeneralization: Drawing broad negative conclusions based on isolated incidents.
- Personalization: Assuming responsibility for events that are beyond personal control.
- Mind-reading: Believing that others hold negative opinions or thoughts about oneself without any evidence.
- All-or-Nothing Thinking: Viewing situations in black-and-white terms, without considering shades of gray.
By recognizing these negative thought patterns, individuals can begin to gain insight into their own thinking processes and understand how they contribute to their emotional well-being.
Challenging Negative Beliefs
Once negative thought patterns have been identified, the next step is to challenge and reframe these negative beliefs. This process involves critically evaluating the evidence supporting these beliefs and considering alternative, more balanced perspectives.
Some effective techniques for challenging negative beliefs include:
- Reality Testing: Examining the evidence for and against a negative belief to evaluate its validity.
- Considering Alternative Explanations: Generating alternative explanations or interpretations of a situation to challenge negative assumptions.
- Decatastrophizing: Examining the likelihood and consequences of the feared outcome to reduce its perceived threat.
- Reattribution: Considering alternative factors that may contribute to a situation, rather than solely blaming oneself.
- Thought Stopping: Actively interrupting negative thought patterns by mentally saying "stop" and replacing them with more positive or realistic thoughts.
By challenging negative beliefs, individuals can begin to shift their perspective and develop a more balanced and adaptive way of thinking. This sets the foundation for the subsequent steps in CBT.
Understanding and addressing negative thoughts and beliefs is just the beginning of the cognitive restructuring process in CBT. In the next step, individuals will explore the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, further deepening their understanding of the impact their thoughts have on their overall well-being.
Step 2: Understanding the Connection Between Thoughts, Feelings, and Behaviors
In the journey of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), it is crucial to comprehend the intricate relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. By exploring this connection, individuals can gain valuable insights into their own patterns and develop strategies for change.
The ABC Model
At the core of understanding the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in CBT is the ABC model. This model suggests that our thoughts (A) about an event or situation trigger emotional and behavioral responses (C). However, it is not the event itself that directly determines our emotions and behaviors; rather, it is our interpretation of the event (B) that influences our emotional and behavioral reactions.
To illustrate the ABC model, let's consider an example:
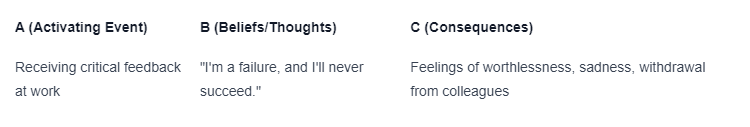
In this scenario, the activating event is receiving critical feedback at work. The individual's beliefs or thoughts about the event lead to negative emotional consequences, such as feelings of worthlessness, sadness, and withdrawal from colleagues.
Examining the Relationship Between Thoughts, Feelings, and Behaviors
In CBT, individuals are encouraged to examine the relationship between their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. By doing so, they can identify any negative or unhelpful thought patterns that may contribute to distressing emotions and maladaptive behaviors.
To explore this connection, individuals are guided to:
- Identify Automatic Thoughts: Automatic thoughts are the immediate, spontaneous thoughts that arise in response to a situation. These thoughts often occur without conscious awareness and can be negative or distorted. Recognizing these automatic thoughts is the first step in understanding their impact on emotions and behaviors.
- Challenge Unhelpful Beliefs: Once automatic thoughts are identified, individuals are encouraged to challenge and evaluate the accuracy and validity of these thoughts. This process involves examining evidence for and against the thoughts, considering alternative explanations, and adopting more realistic and balanced perspectives.
By engaging in this process, individuals can reframe their thoughts and develop healthier and more adaptive beliefs. This, in turn, can lead to positive changes in emotions and behaviors.
Understanding the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors is a fundamental component of cognitive behavioral therapy. By implementing the ABC model and examining their own thought patterns, individuals can gain greater self-awareness and make positive strides towards achieving mental resilience.
Step 3: Restructuring Negative Thoughts
In the journey towards building mental resilience using Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), it is essential to focus on restructuring negative thoughts. This step involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, as well as reframing those thoughts into more positive and balanced perspectives.
Cognitive Restructuring Techniques
Cognitive restructuring techniques are fundamental tools used in CBT to transform negative thinking patterns. These techniques aim to help individuals recognize and replace irrational or unhelpful thoughts with more rational and constructive ones. By doing so, individuals can develop a more balanced and realistic perspective on situations, leading to improved emotional well-being.
Some common cognitive restructuring techniques include:
- Identifying Cognitive Distortions: Cognitive distortions are inaccurate or biased ways of thinking that can contribute to negative thoughts and emotions. By learning to identify and challenge these distortions, individuals can gain a clearer understanding of their thoughts and beliefs. Examples of cognitive distortions include all-or-nothing thinking, overgeneralization, and personalization.
- Examining Evidence: Encouraging individuals to examine the evidence for and against their negative thoughts can help them gain a more objective view of the situation. This involves evaluating the facts and considering alternative interpretations that are more realistic and balanced.
- Decatastrophizing: Catastrophic thinking often involves imagining the worst-case scenario in a given situation. Decatastrophizing involves challenging these catastrophic thoughts and considering more realistic and less extreme outcomes. This technique helps individuals reduce anxiety and develop a more rational perspective.
Reframing Negative Thoughts
Reframing negative thoughts is another crucial aspect of cognitive restructuring in CBT. Reframing involves consciously changing the way one perceives and interprets negative events or situations. By reframing negative thoughts, individuals can create a more positive and adaptive mindset.
Some strategies for reframing negative thoughts include:
- Identifying Alternative Explanations: Encouraging individuals to consider alternative explanations for a situation can help them challenge negative interpretations. This involves looking at the situation from different perspectives and considering other possible reasons for the event or behavior.
- Positive Self-Talk: Engaging in positive self-talk involves replacing negative self-statements with positive and empowering ones. By consciously shifting one's internal dialogue, individuals can develop a more optimistic and supportive mindset.
- Finding Silver Linings: Finding silver linings involves identifying positive aspects or opportunities within challenging situations. This technique helps individuals focus on the potential for growth and learning, fostering resilience and a more positive outlook.
By incorporating cognitive restructuring techniques and reframing negative thoughts, individuals can gradually transform their thinking patterns and build mental resilience. It is important to remember that these techniques may take time and practice to master. Seeking guidance from a qualified CBT therapist can provide additional support and assistance throughout this process.
Step 4: Developing Coping Strategies
As part of the Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) process, developing effective coping strategies is a crucial step in managing negative thoughts and behaviors. By building coping skills and implementing healthy coping mechanisms, individuals can develop resilience and better navigate challenging situations.
Building Coping Skills
Building coping skills is an essential aspect of CBT. Coping skills refer to the strategies and techniques individuals use to manage stress, emotions, and challenging situations. These skills can help individuals respond adaptively to stressors and improve their overall well-being.
Here are some common coping skills that can be developed through CBT:
- Relaxation Techniques: Learning relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation, can help individuals calm their minds and bodies during times of stress.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Developing problem-solving skills enables individuals to identify effective solutions to challenges they encounter. By breaking down problems into smaller, manageable steps, individuals can approach them more effectively.
- Social Support: Building a support system of friends, family, or support groups can provide individuals with a sense of connection and understanding. Sharing experiences and receiving support from others can help alleviate stress and promote resilience.
- Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Engaging in regular physical exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep are important aspects of self-care that contribute to overall well-being and resilience.
Implementing Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Implementing healthy coping mechanisms is a critical part of CBT. These mechanisms are specific actions individuals can take to manage stress and reduce the impact of negative thoughts and emotions. By implementing healthy coping mechanisms, individuals can develop more adaptive responses to challenging situations.
Here are some examples of healthy coping mechanisms:
- Journaling: Writing down thoughts and emotions can provide individuals with a healthy outlet for expressing and processing their feelings. It can also help gain insights into patterns of thinking and identify areas for cognitive restructuring.
- Engaging in Hobbies: Participating in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as painting, playing a musical instrument, or gardening, can serve as a healthy distraction from stressors and promote a positive mindset.
- Practicing Self-Care: Engaging in self-care activities, such as taking a warm bath, practicing self-compassion, or engaging in enjoyable hobbies, can help individuals recharge and maintain emotional well-being.
- Positive Self-Talk: Using positive affirmations and self-talk can help individuals challenge negative thoughts and replace them with more positive and realistic ones. This can contribute to a more positive outlook and improved resilience.
By developing coping skills and implementing healthy coping mechanisms, individuals can enhance their ability to manage stress, regulate emotions, and cope with challenging situations. It is important to remember that everyone's coping strategies may differ, and it may take time and practice to find the techniques that work best for each individual.
Step 5: Practicing Self-Care and Maintenance
To maintain the progress made during Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), it is essential to incorporate self-care practices and ongoing maintenance strategies into your daily life. This step focuses on the importance of self-care and provides strategies to sustain your mental well-being.
Importance of Self-Care
Self-care plays a vital role in maintaining mental resilience and overall well-being. It involves prioritizing activities and practices that promote self-nurturing, relaxation, and stress reduction. By engaging in self-care regularly, you can enhance your ability to cope with challenges and maintain the progress achieved through CBT.
Self-care practices vary from person to person, but some common strategies include:
- Physical Self-Care: Engaging in regular exercise, prioritizing healthy eating habits, getting enough sleep, and attending to any physical health concerns.
- Emotional Self-Care: Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy, expressing emotions in a healthy way, and seeking support from loved ones.
- Social Self-Care: Nurturing healthy relationships, maintaining a support network, and engaging in social activities that bring fulfillment and connection.
- Spiritual Self-Care: Exploring personal beliefs and values, engaging in activities that align with your spiritual or philosophical inclinations, and finding meaning and purpose in life.
By making self-care a priority, you can replenish your energy, reduce stress, and enhance your ability to cope with life's challenges.
Strategies for Ongoing Maintenance
In addition to self-care, there are several strategies you can incorporate into your daily life to maintain the progress achieved through CBT:
- Continued Practice: Regularly practice the cognitive restructuring techniques learned during CBT. Challenge negative thoughts, reframe them into more positive or realistic ones, and apply the ABC Model to understand the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Consistency is key to reinforcing positive changes.
- Reflective Journaling: Maintain a journal to track your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. This practice allows you to gain insights into patterns, identify any triggers or negative thought patterns, and monitor your progress over time.
- Stress Management: Develop and implement effective stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and mindfulness practices. These techniques can help you manage stressors and prevent them from overwhelming you.
- Support System: Maintain a strong support system by nurturing relationships with supportive family members, friends, or support groups. Regularly connect with individuals who understand and encourage your journey to maintain a sense of belonging and support.
- Regular Check-ins: Schedule regular check-ins with yourself to assess your mental well-being, identify any signs of distress or triggers, and address them promptly. Seek professional help if needed, especially if you notice a decline in your mental health.
Remember, self-care and ongoing maintenance are long-term commitments to your mental well-being. By incorporating these strategies into your daily life, you can continue to build and reinforce the resilience developed through CBT, enabling you to navigate life's challenges with greater ease and confidence.
Step 6: Seeking Professional Help
While Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) techniques can be helpful for many individuals, there may come a time when seeking professional help becomes necessary. Professional assistance can provide guidance, support, and expertise in navigating the challenges of mental health. This step focuses on understanding when to seek professional help and finding a qualified CBT therapist.
When to Seek Professional Help
It is important to recognize that CBT techniques may not be sufficient for everyone or every situation. If you find that your mental health concerns are significantly impacting your daily life, relationships, or overall well-being, it may be beneficial to seek professional help. Here are some signs that indicate it may be time to reach out to a qualified mental health professional:
- Persistent Symptoms: If your symptoms, such as anxiety, depression, or other mental health issues, persist for an extended period and significantly interfere with your daily functioning, it is crucial to seek professional assistance.
- Difficulty Coping: If you find it challenging to cope with your emotions, thoughts, or behaviors despite trying CBT techniques on your own, a mental health professional can provide additional strategies and support.
- Risk of Harm: If you experience thoughts or feelings of self-harm, suicide, or harming others, seeking professional help is of utmost importance. Reach out to a mental health professional or a helpline immediately.
- Complex Mental Health Conditions: Certain mental health conditions, such as severe depression, bipolar disorder, or personality disorders, may require specialized treatment and expertise. Professional help can ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Remember, seeking professional help is not a sign of weakness but a proactive step towards cultivating better mental health. It is always better to reach out sooner rather than later to prevent symptoms from worsening.
Conclusion
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a powerful tool for managing negative thoughts and emotions and building resilience. By following the six steps outlined in this article, individuals can develop an understanding of their thought patterns, challenge negative beliefs, build coping skills, implement healthy coping mechanisms, prioritize self-care and ongoing maintenance, and know when to seek professional help.
While CBT can be practiced independently, seeking guidance from a qualified CBT therapist can provide additional support and assistance throughout the process. It is important to remember that everyone's journey with mental health is unique, and there is no one-size-fits-all approach. However, by incorporating the techniques discussed in this article into daily life and maintaining a commitment to mental well-being, individuals can cultivate greater resilience and navigate life's challenges with greater ease.
Sources:
https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-cognitive-behavior-therapy-2795747
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/cognitive-behavioral-therapy/about/pac-20384610









